
A cohort is a group of users who share a common event or experience within a defined time frame. Unlike segments, which group users by demographics or static characteristics, cohorts are time-bound and behavior-specific.
Segments: Groups based on demographics or static traits (e.g., all women aged 60+).
Cohorts: Groups based on a shared experience or action within a timeframe (e.g., women aged 60+ who made their first purchase in November 2020).
Users who made their first purchase in the last 30 days.
People who attended a concert in a specific city in 2017.
Customers who started using a service during a financial recession.
Cohort analysis studies the behavior of specific cohorts over time to identify patterns, trends, and engagement levels. It allows marketers to:
Measure repeat purchases and user retention.
Compare performance across cohorts (e.g., acquisition campaigns).
Normalize data to detect real improvements in engagement, independent of overall growth.
Track first-time shoppers month by month.
Analyze how quickly they make a second purchase.
Identify cohorts with higher repeat rates and optimize strategies to reduce the gap between purchases.
Rows = Cohorts: Each row represents users who performed a first event on a specific date or within a time frame.
Day 0: Refers to the date of the first event for that cohort. Subsequent columns track behavior over days, weeks, or months.
Colors Indicate Engagement: Darker shades represent higher activity percentages; lighter shades indicate lower engagement.
Define Your Questions: Identify the specific user behavior or trend you want to analyze.
Example: Are renewal rates low for users acquired in a certain month?
Are conversion rates low for users on specific devices?
Determine Relevant Events and Attributes: Track the actions that answer your questions.
Example: “Purchase Complete” event, filtered by device or acquisition channel.
Observe and Compare Cohorts Over Time:
Create cohorts based on first events and analyze subsequent behavior.
Compare cohorts by acquisition month, device, or other attributes to identify patterns.
Draw Insights and Take Action:
Identify high-performing cohorts and replicate strategies.
Detect underperforming cohorts and investigate causes.
Start small and scale cohort analysis gradually.
Ensure data is relevant, clean, and reliable.
Focus on broad behavioral trends before diving into granular metrics.
Use cohort insights to improve engagement, retention, and conversion strategies.
A funnel represents the steps a user takes on your website, app, or through marketing campaigns to reach a specific goal, such as a signup, purchase, or subscription renewal. Funnels help identify where users drop off and optimize for higher conversions.
Drop-offs: Most users do not complete all funnel steps.
End Goal: The desired outcome for the user (e.g., purchase, signup).
Optimization: Focus on quality leads and reducing drop-offs at each step.
Acquisition Funnel – Brings prospects to your platform.
Focus: Awareness and engagement.
Tactics: Targeted campaigns, landing pages, social proof, retargeting ads.
Activation Funnel – Converts prospects into customers.
Focus: Build trust and highlight product value.
Tactics: Product demos, tutorials, blog posts, testimonials, email nurturing.
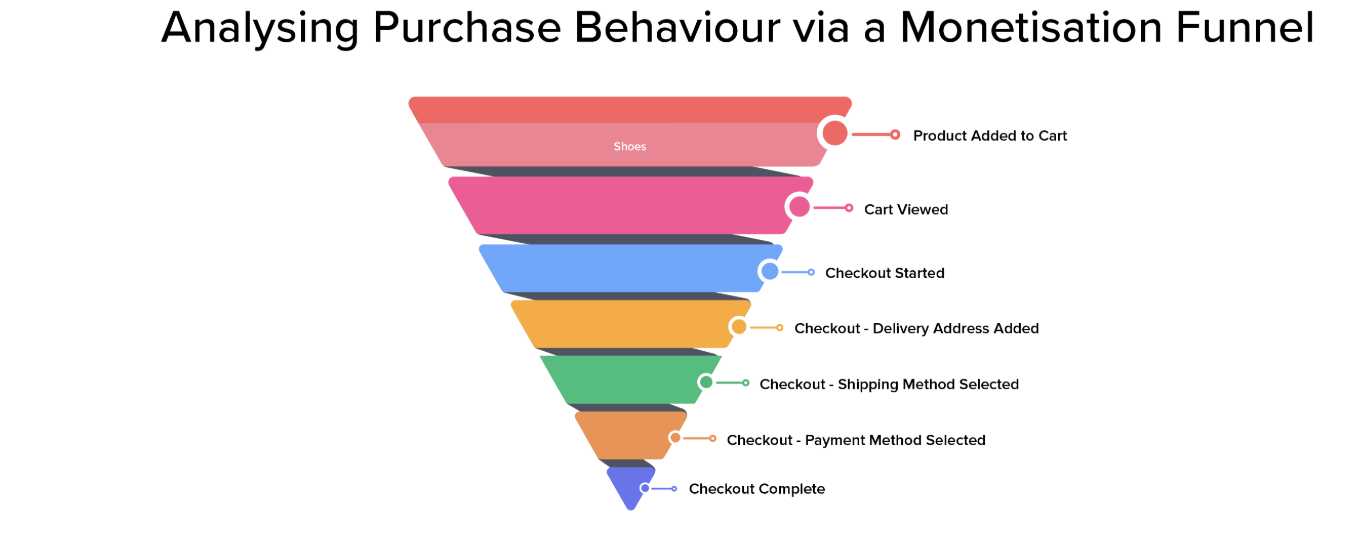
Monetization Funnel – Drives first purchase and ongoing engagement.
Focus: Pre-purchase and post-purchase journeys.
Tactics: Post-purchase engagement, loyalty programs, repeat purchase campaigns, referrals.
Note: Retention marketing is more cost-effective than acquiring new users, as it builds on existing relationships.
Identify the End Goal: Define the action you want users to complete.
Map User Paths: Determine all ways users can reach the goal across your app, website, and campaigns.
Define Funnel Steps: List all events users must perform to reach the goal. Each step becomes part of the funnel.
Analyze Funnel: Track metrics like overall conversion rate, drop-off rate per step, and average conversion time.
Optimize Funnel: Form hypotheses for drop-offs, test changes, and implement improvements.
User adds a product to the cart but doesn’t complete checkout.
Funnel analysis shows the highest drop-off occurs between Payment Method Selected and Checkout Complete.
Possible causes:
Broken payment gateway link
Bank transaction errors
Connectivity issues
Solutions:
Offer Cash on Delivery or alternative payment gateways.
Provide options for delayed online payment.
Send personalized messages encouraging checkout completion.
Funnels track user behavior across the lifecycle.
Different funnel types (Acquisition, Activation, Monetization) help identify issues at specific stages.
Regular funnel analysis helps reduce drop-offs, improve conversions, and optimize retention strategies.
Post-purchase engagement drives repeat purchases and referrals, amplifying customer lifetime value.